Plantain Vs Banana - What's The Real Difference?
Have you ever stood in the produce section, perhaps a bit puzzled, looking at those longer, greener items next to the familiar yellow bananas? It's a fairly common sight, that moment of wondering if they are just big bananas or something else entirely. Well, as a matter of fact, these two tropical fruits, while sharing a family connection, have some rather distinct characteristics that set them apart in how they look, how they taste, and how people use them in the kitchen.
People often get these two mixed up, and it's easy to see why, too. They both come from the same general plant group, and they certainly bear a resemblance to each other. However, once you get past the initial visual similarity, you start to notice some truly interesting differences, particularly when it comes to their texture and what you might do with them in a meal. One is typically enjoyed as a sweet, handheld snack, while the other tends to be a foundational ingredient in cooked dishes, more like a vegetable than a fruit you'd just peel and eat.
This little chat will help clear up some of that confusion, giving you a better idea of what makes each of these unique. We will explore their appearances, how they are generally eaten, and even touch on some of the good things they bring to your body. So, if you have ever been curious about these two close relatives, you will find some helpful thoughts here about what sets the plantain apart from its more common banana cousin, and how each plays a part in different food traditions.
Table of Contents
- Are Plantains Just Bigger Bananas?
- Appearance and Texture - Plantain vs Banana
- What Makes Plantain a Staple Food?
- Culinary Uses - Plantain vs Banana
- How Do Plantains Benefit Your Health?
- The Unexpected Medicinal Plantain
- How Do Nutrients Compare - Plantain vs Banana?
- Nutritional Goodness - Plantain vs Banana
Are Plantains Just Bigger Bananas?
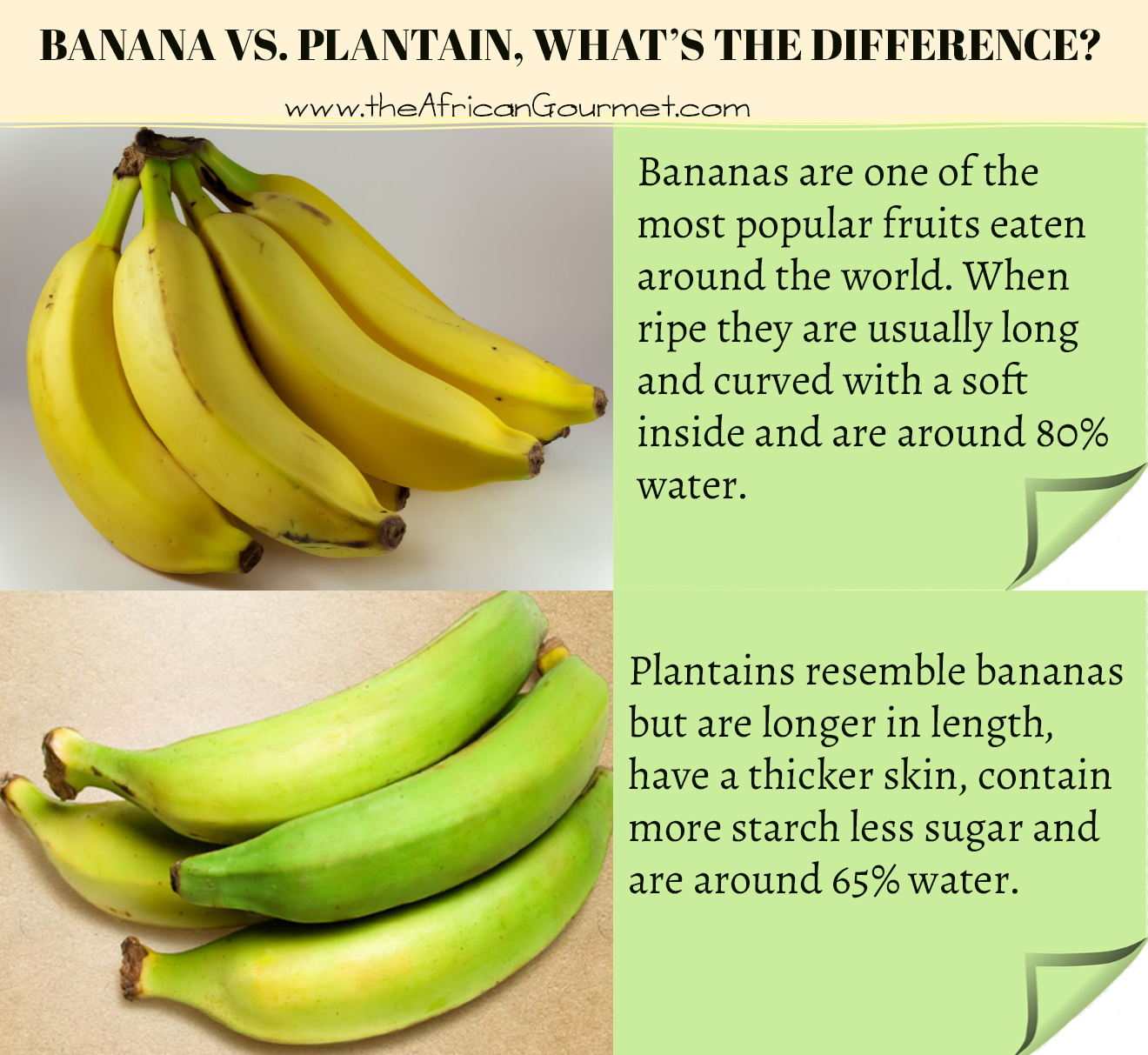
When you first see a plantain, it’s really easy to think it’s just a larger version of the bananas we typically snack on. They do, in fact, look quite alike, sharing that familiar curved shape and a peelable skin. However, there are some pretty clear distinctions that go beyond just their size. Plantains are, generally speaking, longer and also have a bit more girth than the common dessert banana. This visual difference is usually the first clue that you might be looking at something a little different from your everyday yellow fruit, too.
One of the most noticeable things about plantains, besides their overall size, is the thickness of their skin. It tends to be quite a bit more substantial than the skin on a regular banana, which can make them a little trickier to peel, especially when they are not fully ripe. This thicker outer layer is just one of those physical traits that hints at their different nature, suggesting they are meant for a different kind of preparation. So, while they might appear similar at a glance, these physical attributes are a fairly good indicator of their distinct identities.
Appearance and Texture - Plantain vs Banana
Beyond just being larger, plantains typically present with a skin that is a deeper green when unripe, often turning to yellow and then black as they ripen, but even when fully ripe, their texture inside remains somewhat firm. The common dessert banana, by contrast, usually starts green and quickly turns to a bright yellow, becoming quite soft and sweet as it ripens. This difference in how they look and feel at various stages of ripeness is a key part of telling them apart, you know.
The internal texture is another big giveaway, actually. A plantain, even when it is quite mature, will still have a much firmer, denser flesh compared to the soft, creamy inside of a ripe banana. This firm quality is directly related to its higher starch content, which is a really important characteristic for how it is used in cooking. You won't find a plantain getting mushy in the same way a banana does when it gets very ripe; it holds its shape much better, which is pretty useful for certain dishes.
What Makes Plantain a Staple Food?
Plantains are a very important group of banana varieties that serve as a primary food source in many tropical regions around the world. They are not just a casual snack; they are a fundamental part of daily meals for countless people, providing essential sustenance. In places like the Dominican Republic, for example, the plantain is a truly central part of the diet, used as much as, or perhaps even more than, rice. This shows just how deeply integrated it is into the food culture of these areas, so it's almost like a main character on the plate.
The reason plantains hold such a significant position as a staple food comes down to their versatility and their nutritional value. They can be cooked in so many different ways, which makes them incredibly adaptable for various dishes and meal times. Their ability to provide a substantial amount of energy and other good things for the body also makes them a reliable and dependable food source, particularly where other food options might be less available. It's a food that can truly sustain a population, you see.
Culinary Uses - Plantain vs Banana
The most significant difference between plantains and bananas, perhaps, lies in how they are prepared and eaten. The common dessert banana is typically enjoyed raw, peeled and eaten straight out of its skin as a sweet fruit. Its soft texture and sugary taste make it a perfect quick snack or an addition to smoothies and desserts. That is really what most people think of when they hear the word "banana," and it’s a fairly simple way to enjoy it, too.
Plantains, on the other hand, have a much higher starch content and are not usually eaten raw. Their flavor is more savory, and they require cooking to become palatable. They are often harvested when they are still unripe and green, nearing their full size but before they develop much sweetness. This means they need to be cooked, often by frying, boiling, baking, or roasting, to soften their starchy flesh and bring out their unique flavor. Dishes like Mangu and Sancocho, where plantain plays a very important role, are good examples of how this fruit is cooked and enjoyed as a main component of a meal, actually.
There are quite a few baked plantain recipes you can find online, offering plenty of ways to experiment and discover what you might like best. With the right preparation, plantains can be a really safe and tasty addition to your cooking repertoire. Whether they are green and starchy or a bit riper and sweeter, their use in the kitchen is what truly sets them apart from their more familiar banana cousins, just a little bit different in their approach to the plate.
How Do Plantains Benefit Your Health?
Plantains, whether we are talking about the fruit or the herb, offer some pretty interesting benefits for your body. The edible fruit, which is a significant food crop, contains a good amount of potassium and fiber, making it a valuable part of a balanced eating plan. These components are quite important for general well-being, helping with various bodily functions. So, while they might be a staple food for their substance, they also bring a good deal of goodness to the table.
Some of the unexpected benefits of the plantain fruit, according to dietitians, include giving you a bit of an energy boost and providing prebiotics. Prebiotics are substances that help feed the good bacteria in your gut, which is a pretty important part of keeping your digestive system happy and healthy. Learning about these uses and potential good things that plantains offer, including what amounts might be helpful, really helps you appreciate this food beyond just its taste and texture, you know.
The Unexpected Medicinal Plantain
Now, this is where things get a little bit interesting and sometimes confusing, as the word "plantain" can also refer to a common garden weed, known scientifically as Plantago major. This particular plantain is not the banana-like fruit we have been discussing, but a completely different botanical entity. This garden plant has been recognized for centuries for its potential to help with various bodily needs. It's quite surprising for many to learn that a common weed can have such useful qualities, that is for sure.
This plantain herb, or plantain weed, may offer some health benefits, such as helping with digestion, making wounds heal better, and reducing swelling. People have used this plant as a medicinal herb, relying on its natural properties to support the body's own processes. There are proven uses for this specific plantain, and understanding how to use it as a medicinal herb can be quite insightful. It’s a different kind of plantain entirely, but one that has its own set of valuable characteristics, too it's almost like a hidden gem in your backyard.
How Do Nutrients Compare - Plantain vs Banana?
When you look at the nutritional content of plantains and bananas, you will find that they are actually quite similar in many ways, given their close genetic relationship. Both of these tropical fruits provide a good amount of important things your body needs to function well. They share some of the same key vitamins and minerals, which is pretty neat considering how different they are in terms of how we usually eat them. So, in some respects, they are like nutritional cousins, offering similar building blocks for your health.
Both bananas and plantains are considered good sources of dietary fiber, which is really helpful for keeping your digestive system moving along smoothly. However, plantains tend to have a slightly higher fiber content, which could be a small advantage for those looking to increase their fiber intake. This difference, while not huge, does contribute to their overall nutritional profile and how they might fit into different eating plans, just a little bit more of that good stuff.
Nutritional Goodness - Plantain vs Banana
Plantains offer a range of good things for your body, similar to their banana cousins. These include potassium, which is important for heart health and muscle function; magnesium, which plays a part in many bodily processes; folate, which is vital for cell growth; and vitamin C, known for its role in immune support. While there are some differences in the amounts of these nutrients, the overall picture is that both are quite beneficial additions to your diet, providing a good mix of things your body needs to stay healthy, you know.
The key things to remember about the differences in nutrients and how they are generally eaten are that bananas are typically sweeter, have a softer texture, and are usually enjoyed raw. Plantains, on the other hand, are starchier, have a more savory flavor, and absolutely need to be cooked before you eat them. It is also a good idea to think about how ripe they are, as this can affect both their taste and their nutritional makeup, as well as how you might want to prepare them. So, while they come from the same family, their paths to your plate are quite distinct, really.
This discussion has covered the main differences between plantains and bananas, including how they look, how they taste, and how they are used in the kitchen. We have also touched upon the different types of "plantain" and their unique health benefits, from the fruit's nutritional value to the medicinal uses of the garden herb. We also looked at how their nutritional contents compare, showing that both bring good things to your diet, just in slightly different ways. This should give you a clearer picture of these fascinating tropical items.
Plantain Banana

Plantain Vs Banana Taste

Banana vs Plantains: What’s the Difference? | MIC Food