Understanding Cell Block 1: From Life's Building Blocks To Excel's Core Functions
Have you ever stopped to think about the tiny, fundamental pieces that make up everything around us? It's almost amazing how much detail goes into the basic parts of life and even the tools we use every day. We're going to talk about "cell block 1" today, which, in a way, points to the very first or most basic unit in different areas. This isn't about a physical place, but rather the foundational concept of a "cell," whether we're talking about living things or the digital world of spreadsheets.
For living organisms, the cell stands as the smallest living unit, a truly incredible building block that handles all sorts of vital processes. Think about it: your body, a tree, even a tiny bacterium – they all start with cells. These microscopic powerhouses are, you know, responsible for keeping everything going, from getting energy to making new copies of themselves. They truly are the basic units of all life on our planet.
Then, there's the "cell" in a spreadsheet, like in Excel. This kind of cell is also a basic unit, holding a piece of data or a formula. Just like biological cells have specific jobs, an Excel cell has its own purpose within a larger structure. It's really quite fascinating how a single term can have such deep meaning across very different fields, isn't it? Both represent a core, foundational element, which is what we mean by "cell block 1" in these contexts.
Table of Contents
- The Biological Cell: Life's First Building Block
- The Excel CELL Function: Your Data's Information Block
- Connecting the "Cell Blocks": Why Both Matter
- Questions People Often Ask
The Biological Cell: Life's First Building Block
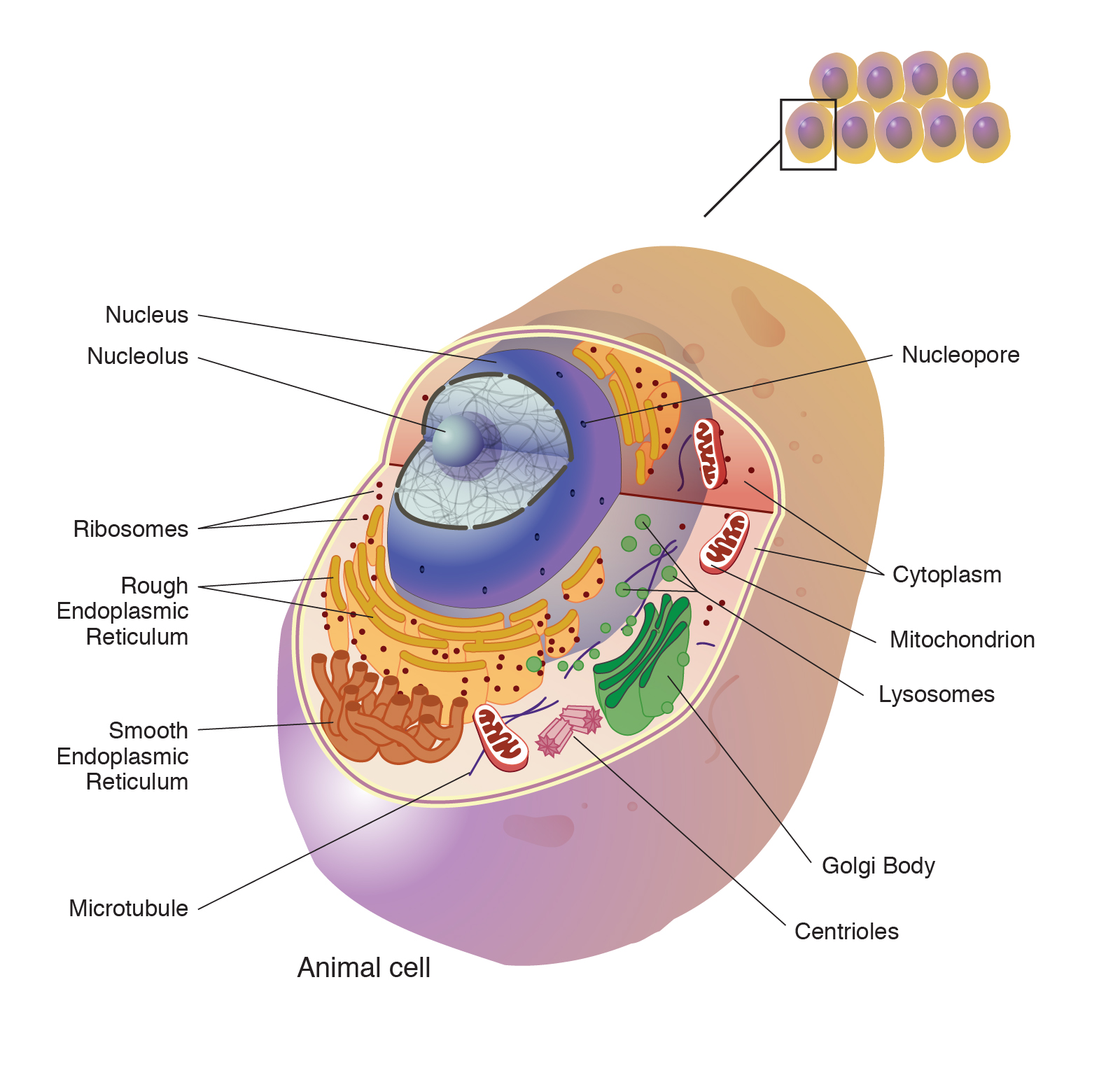
When we talk about "cell block 1" in biology, we're really focusing on the very beginning of life itself. A cell is, you know, the smallest living organism and the basic unit of life on Earth. Trillions of these tiny units make up the human body, providing structure and taking in nutrients from food. They are, in fact, the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms, responsible for various life processes and containing essential biological parts. Every living thing, from the smallest single-celled creature to the largest whale, is made of these fundamental units, which is quite a thought.
The idea that all living things are made of cells wasn't always obvious. Cell theory, developed in 1839 by Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells. This theory also says that cells are the fundamental unit of structure for life. This was, you know, a huge step in how we understood biology, truly changing how people thought about living matter. It laid the groundwork for so much of what we know about life today, giving us a clear starting point for biological study.
Inside every cell, there's a host of structures known as organelles. These tiny parts each have a specific job, helping the cell carry out essential functions such as energy conversion, reproduction, and protein synthesis. All cells are capable of replication, protein synthesis, and motility, which is pretty cool when you think about it. They are, in a way, self-contained little factories, each working together to keep the cell alive and functioning. This intricate internal organization allows them to perform incredibly complex tasks.
Cells emerged on Earth about 4 billion years ago, which is an incredibly long time. They are broadly categorized into two main types, though we won't get into all the specifics here. Every cell has essential structures that are the same, much like every house has a kitchen and a living room. Learning how cell function depends on a diverse group of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and sugars helps us understand life itself, you see. This understanding is, arguably, the very first step in grasping biology as a whole.
What Makes a Cell "Work"?
A cell is a mass of cytoplasm that is bound externally by a cell membrane. Usually microscopic in size, cells are the smallest structural units of living matter. This outer boundary controls what goes in and out, which is, you know, super important for keeping the cell healthy. The cell membrane acts like a gatekeeper, deciding what enters and leaves, protecting the cell's inner environment. Without this careful control, a cell simply couldn't survive.
The cytoplasm inside is where much of the cell's activity takes place, sort of like the main work floor. Within this jelly-like substance, organelles float and perform their duties. The ability of cells to carry out essential functions is what makes them so vital. They convert energy, which means they take in food and turn it into fuel. This energy is then used for everything else the cell needs to do, like growing or repairing itself. Energy conversion is, basically, a non-stop job for every living cell.
They also reproduce, creating new cells to grow or replace old ones. This process, known as cell division, is fundamental to life, allowing organisms to develop and heal. Protein synthesis, the making of proteins, is another key task, as proteins do so much of the work inside a cell. These are, in some respects, the core jobs of any living cell, ensuring its continued existence and the health of the larger organism it belongs to. A single cell is often a complete living unit, capable of all these amazing feats on its own.
From a biological standpoint, the cell is the fundamental unit of life, forming the building block of all living organisms. This basic unit provides structure for the body and helps in countless ways. Understanding these basic elements, or "cell block 1" of biology, gives us a really strong foundation for understanding all life forms, you know, from the smallest bacteria to the largest whales. It's the starting point for exploring the vast and complex world of living things, allowing us to appreciate their shared origins and varied forms.
The Excel CELL Function: Your Data's Information Block
Now, let's shift our focus to "cell block 1" in the digital world, specifically with the Excel `CELL` function. This function is, you know, an Excel information function that will extract information about a cell’s location, contents, or formatting. It's a handy tool for getting details about any cell in your worksheet, which can be pretty useful for data checking or setting up complex sheets. The `CELL` function returns information about a cell in a worksheet, which is quite helpful for automation.
The `CELL` function takes two arguments. One determines the type of information to be returned, which is specified as `info_type`. For example, you might want to verify that a cell contains a numeric value instead of text before you use it in a calculation. This function can help you do just that, giving you a bit of control over your data quality, you see. The `info_type` argument can specify things like "address" for the cell's location, "contents" for what's inside, or "format" for how it looks, among others. It’s a versatile tool for inspecting your data at a very granular level.
The tutorial shows how to use the `CELL` function in Excel to retrieve various information about a cell such as cell address, contents, formatting, location, and more. This function returns information about the formatting, location, or contents of a cell. It can get things like the address, or what's actually written inside the cell. It's a bit like asking a cell, "Hey, what are you all about?" This kind of capability is especially useful when you're working with large datasets and need to quickly understand specific cell properties without manually checking each one. It offers a programmatic way to interact with cell information.
Practical Uses of the CELL Function
The Excel `CELL` function helps to display various properties of a given cell. You can ask it to return the location, formatting, or contents of the cell. For example, suppose that you are checking a large spreadsheet and need to quickly see if certain cells have specific formatting applied. This function can help automate that check, saving you a lot of time, honestly. It can be integrated into larger formulas to make decisions based on cell properties, which is really powerful.
It's very useful for data validation or for building dynamic formulas. For instance, you could use it to check if a cell is empty or if it contains an error. This kind of check helps ensure your spreadsheet works as expected and avoids problems down the line. It's a rather practical way to get insights into your data without manually clicking on every single cell. You can set up rules that automatically flag cells that don't meet certain criteria, making your spreadsheets more robust and reliable. This makes managing complex data much simpler.
From this article, you will get a brief idea of Excel cells including selecting, inserting, deleting, and customizing cells and cell contents. The `CELL` function adds another layer to this understanding, allowing you to programmatically inspect cells. It’s a good tool to have in your Excel toolkit, especially when you are dealing with complex data sets, you know. Mastering this function can really improve your efficiency and accuracy when working with spreadsheets, making you a more capable data handler.
Connecting the "Cell Blocks": Why Both Matter
It's interesting to see how the concept of "cell block 1" applies to both living organisms and digital data. In both cases, we are talking about a fundamental, basic unit that forms a larger structure. Whether it's a biological cell making up an organism or an Excel cell making up a spreadsheet, understanding these core components is, you know, truly important for understanding the whole. Both types of "cells" are indispensable for the systems they belong to, acting as foundational elements.
Both types of "cells" carry out essential functions. Biological cells perform life processes, while Excel cells store and process data. Both are, in a way, building blocks that enable more complex systems to operate. This parallel helps us appreciate the importance of foundational knowledge, no matter the field. It’s quite a neat connection, really, showing how similar principles can apply across vastly different domains. Recognizing these basic units helps us grasp the bigger picture more easily.
Knowing about the biological cell, the smallest living unit, helps us appreciate the amazing complexity of life. Similarly, understanding the Excel `CELL` function, a basic data unit tool, helps us manage and analyze information more effectively. Both are about getting to the core of things, which is, you know, always a good idea. This fundamental understanding empowers us to work with life and data in more informed and powerful ways, truly starting from the ground up.
Questions People Often Ask

Animal Cell Organelles by Teach Simple

What Cell-to-Cell Communication teaches us about human society
Cell